What is a taxonomy?
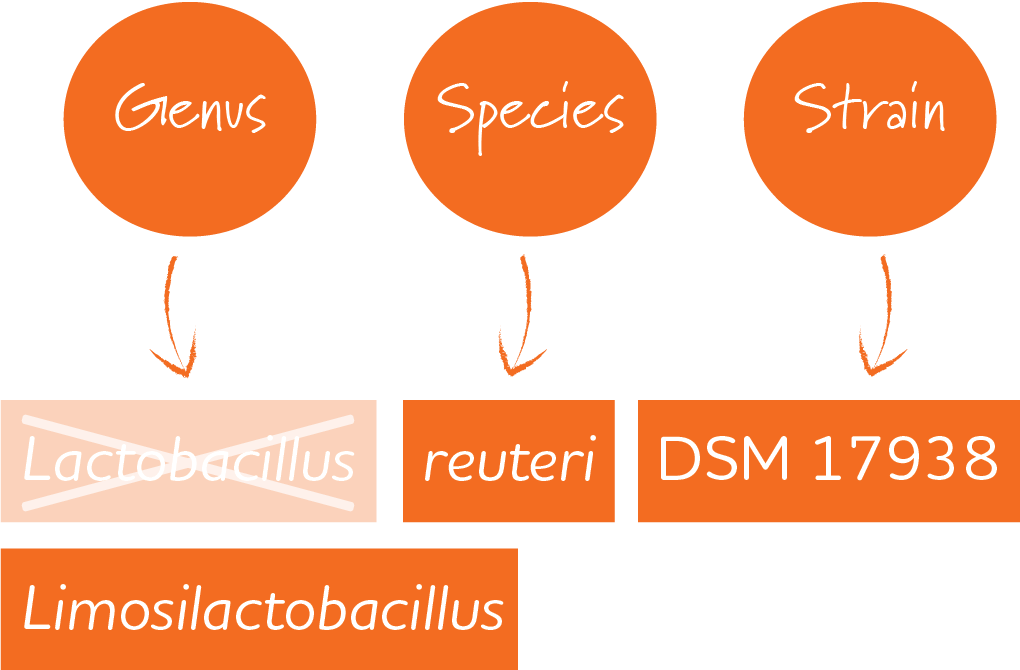
Taxonomy is known as the science for naming, grouping and classification of organisms. The taxonomy of lactic acid bacteria are divided into genus (Limosilactobacillus), species (reuteri) and strain (DSM 17938).
What has changed?
Several probiotic bacteria previously known as Lactobacillus have been renamed. Lactobacillus reuteri is now known as Limosilactobacillus reuteri.
However, it’s essential to note that it is only the genus part, Lactobacillus, that has changed; species and strain names remain the same, and of course, the organisms themselves, including their effects and safety.
Why the change of name?
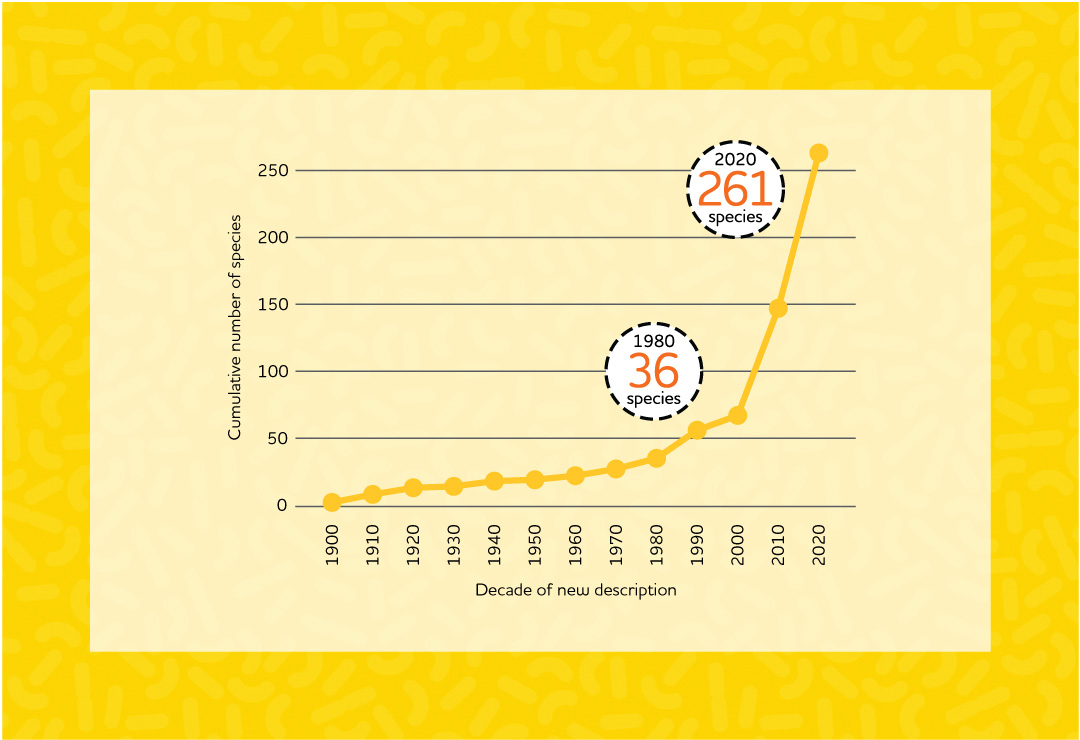
The first Lactobacillus species was named in 1901. Initially, Lactobacillus and other bacteria genera were identified by their shape, colour, or chemical reactions. The majority of the 20th century was spent discovering new Lactobacillus species, yet by 1980, only 36 had been identified.
In recent years, improved tools, such as DNA and genome sequencing, have enabled scientists to discover many new types of bacteria. Consequently, as of March 2020, the genus Lactobacillus included 261 species.
Scientists found that these species were extremely diverse on a phenotypic, ecological, and genotypic level, which was problematic. According to scientists, the species historically classified and grouped as Lactobacillus differed too much from one another. In response, a group of experts decided to modify the Lactobacillus genus and create a more accurate and organised group.
New genera
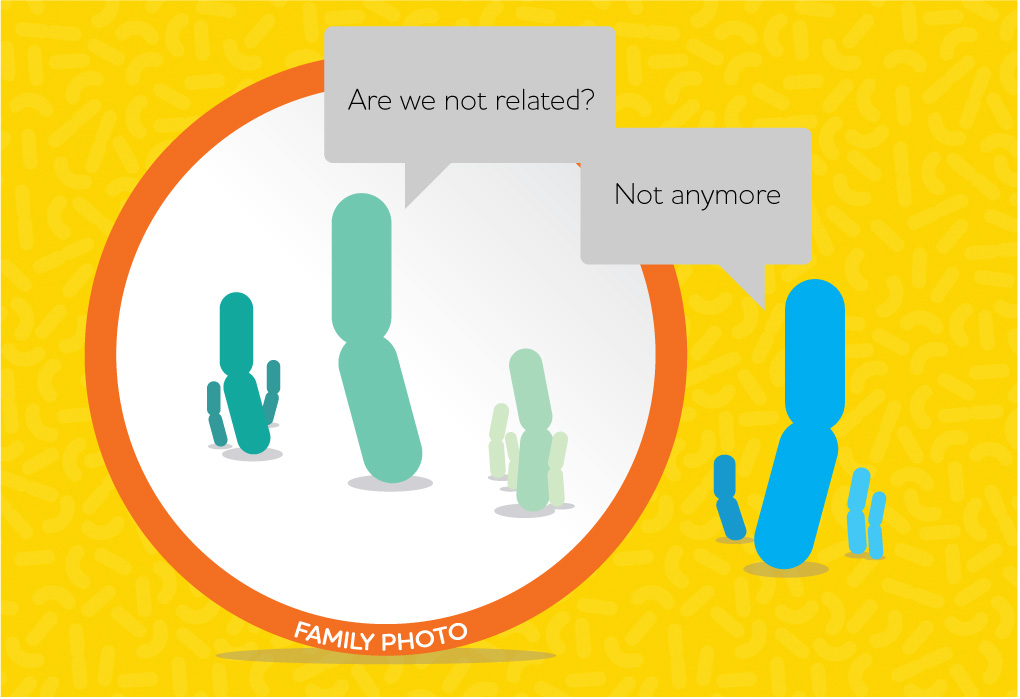
The Lactobacillus genus became too crowded, making it difficult to distinguish members of the genus due to differences in their appearance and properties. Scientists concluded that a taxonomy change was necessary and suggested new genus names.
Eventually, it was decided that only 35 species of Lactobacillus should be included in the genus. Other species within the genus were divided into 23 new genera with new genus names.
Fortunately, the current and former names are quite similar and their short forms will remain the same (L. reuteri is still named L. reuteri).
Limosilactobacillus - The slimy bacteria
In Latin, the word Limosus means 'slimy', which perhaps doesn’t sound very appealing. However, the 'slime' produced by all Limosilactobacillus species is a substance known as exopolysaccharides (EPS).
The production of EPS comes from sucrose and supports biofilm formation in the digestive tract. Some probiotic health benefits, such as the effects on the immune system and inhibition of pathogenic bacteria, have been connected to EPS.
As of today, 17 species have been identified within the genus of Limosilactobacillus, with BioGaia's L. reuteri being one of the strains.
Does the name change have any consequences?
What does this name change mean for people who use probiotic dietary supplements and for doctors who prescribe them? In most cases, the name change will not have any impact.
A consumer will be able to notice the name change on the packaging label or in the product information. However, there is no change in the content of the probiotic. Transitioning from the previous taxonomy to the new one will likely take years.
It is hoped that this change will make it easier to understand the properties of certain probiotic strains and how they belong to a specific genus.
For information about specific probiotics, we recommend searching for clinical trials using both the former and current strain names.
Further reading
The article describing the new taxonomy (published in IJSEM) includes an overview of the new strain names. There is also a tool that allows you to check the conversion from ‘old’ to ‘new’ or vice versa.
For more information, please read this article on ISAPP Science Blog and ISAPP's infographic. If you have questions, please contact [email protected].
